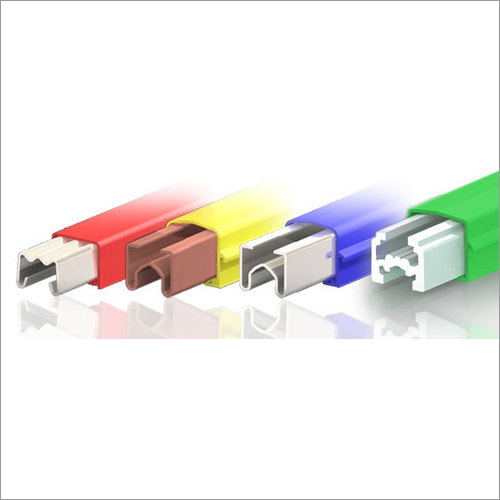

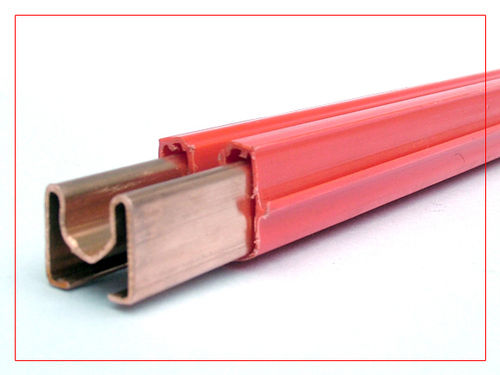
DSL Busbar System
Product Details:
- Surface Finish Color Coated
- Application Industrial
- Protection Level IP54
- Rated Voltage 400 Volt (V)
- Color Red Yellow Blue Green
- Warranty 1 Year
- Material Plastic
- Click to view more
X
DSL Busbar System Price And Quantity
- 9 Meter
DSL Busbar System Product Specifications
- Plastic
- 400 Volt (V)
- Red Yellow Blue Green
- Color Coated
- Industrial
- 1 Year
- IP54
DSL Busbar System Trade Information
- Cheque
- 500 Meter Per Week
- 4 Days
- Yes
- Free samples available with shipping and taxes paid by the buyer
- LONG WOODEN CASE WITH TIGHT PACK
- AN ISO 9001 : 2015 CERTIFIED COMPANY
Product Description
A DSL (Direct Supply Line) busbar system is a type of electrical power distribution system commonly used in industrial and commercial settings to deliver electricity to various equipment and machinery. It is designed to provide a safe and efficient means of supplying power to different loads.
Here are some key features and components of a DSL busbar system:
1. Busbar: The central component of the system is the busbar itself, which is typically a metal conductor (often made of aluminum or copper) in the form of a bar or a series of bars. These conductors are designed to carry high levels of electrical current.
2. Enclosure: The busbar is housed within an enclosure, which provides protection against physical damage, dust, and moisture. The enclosure may be made of materials like metal or plastic.
3. Supports and Insulators: The busbar is supported and insulated from the enclosure using insulators. This prevents the busbar from coming into direct contact with the enclosure, reducing the risk of electrical faults.
4. Tap-Off Units: Tap-off units or connectors are used to access the power from the busbar for connecting loads. These connectors allow for the easy and flexible connection of equipment to the busbar system.
5. Isolation Switches: Isolation switches are installed at various points in the busbar system to isolate specific sections for maintenance or in case of a fault. They ensure that power can be safely disconnected for servicing without affecting the entire system.
6. Current Rating: DSL busbar systems are designed with different current ratings to accommodate a wide range of power distribution needs. The current rating of the busbar depends on the capacity of the loads it is intended to supply.
7. Voltage Rating: The voltage rating of a DSL busbar system is determined by the voltage of the electrical supply it is connected to. Common voltage ratings include 400V, 690V, and 1000V.
8. Flexibility: DSL busbar systems are known for their flexibility, which allows for easy reconfiguration and expansion of the power distribution network. New loads can be added or relocated without the need for extensive rewiring.
9. Efficiency: Busbar systems are more efficient than traditional cable systems because they offer lower electrical resistance, reducing energy losses and heat generation.
DSL busbar systems are commonly used in manufacturing facilities, data centers, distribution centers, and other industrial applications where a reliable and flexible power distribution system is essential. They offer advantages such as enhanced safety, reduced installation time, and improved maintenance capabilities compared to traditional cable-based power distribution systems.
DSL Busbar System FAQ:
Q. What is a DSL busbar system?
Ans: A DSL busbar system is an electrical power distribution system used in industrial and commercial settings to efficiently and safely distribute electrical power to various equipment and machinery. It consists of a busbar, enclosures, tap-off units, insulators, and other components.
Q. How does a DSL busbar system work?
Ans: A DSL busbar system works by delivering electrical power from the main supply to various loads using a central conductor (busbar). Tap-off units are used to connect equipment to the busbar, and the system is designed to be flexible for easy configuration and expansion.
Q. What are the advantages of a DSL busbar system over traditional cabling?
Ans: Some advantages of DSL busbar systems include higher efficiency, lower electrical resistance, reduced energy losses, easier installation, flexibility for adding or relocating loads, and improved safety with proper enclosures and isolation switches.
Q. Where are DSL busbar systems commonly used?
Ans: DSL busbar systems are commonly used in industrial settings, such as manufacturing facilities, data centers, distribution centers, and other commercial and large-scale applications where a reliable and flexible power distribution system is required.
Q. What is the typical voltage and current rating of DSL busbar systems?
Ans: The voltage and current ratings can vary, but common voltage ratings include 400V, 690V, and 1000V. The current rating depends on the capacity of the loads it needs to supply and can range from a few hundred amperes to several thousand amperes.
Q. How do you maintain a DSL busbar system?
Ans: Maintenance typically involves periodic inspections of the busbar, tap-off units, and enclosures to ensure they are in good condition. Isolation switches should be tested regularly, and any damaged components should be replaced promptly. Maintenance procedures should follow the manufacturer's recommendations.
Q. Can a DSL busbar system be expanded or reconfigured easily?
Ans: Yes, one of the key advantages of DSL busbar systems is their flexibility. They can be easily expanded or reconfigured by adding or relocating tap-off units to accommodate new loads or changes in the layout.
Q. What safety precautions should be taken with DSL busbar systems?
Ans: Safety measures include proper grounding, regular inspection of insulation and connections, using safety barriers to prevent accidental contact with live parts, and following lockout/tagout procedures when performing maintenance.
Q. Are DSL busbar systems suitable for outdoor use?
Ans: DSL busbar systems are typically designed for indoor use or in environments protected from the elements. If outdoor use is required, special enclosures and weatherproofing measures should be considered.
Q. Are there different types of DSL busbar systems available?
Ans: Yes, there are different designs and manufacturers of DSL busbar systems. These may vary in terms of materials, features, and specifications. Choosing the right type depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
 08045801632
08045801632
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS
